Through its business activities, the Group is working to reduce GHG
(greenhouse gas) emissions, which is an important issue of global scale. In
response to market and customer demands for environmental friendliness, we
will integrate the design, procurement, and manufacturing processes for our
products and services to provide added value, such as energy savings. In
addition, to reduce GHG emissions in Scope 1 and 2, we will pursue efficient
energy use by harnessing the creativity and ingenuity of all our employees.
|Environmental policies
-
We will evaluate the environmental impact of all our business activities and
the products we provide to our customers at during production, use, and
disposal, and strive to save resources and energy, reduce waste, and prevent
pollution.
-
We will establish and maintain a PDCA cycle by setting environmental
objectives and targets for these initiatives.
-
In addition to complying with environmental laws and regulations,
ordinances, industry codes of conduct, and agreements with local
communities, we will establish and maintain independent management standards
wherever possible.
-
We will establish an environmental management system in which all employees
participate, using audits and reviews to make improvements on an ongoing
basis.
-
We will provide education to all employees to improve their awareness of the
environment and the environmental management system, as well as asking our
affiliates and partner companies for their understanding and cooperation.
- These environmental policies shall be publicly disclosed.
Environmental policies in each district
Our Nasu, Yaita, and Sano plants have drawn up their own environmental
policies based on the company-wide policies, taking into account the
characteristics of the manufacturing they perform and consideration for
the surrounding environment. Each district has established an environmental management system in line with the policy and is continually promoting environmental improvement initiatives.
ISO 14001 compliance status
|
Location |
Date acquired
|
| Nasu Plant |
December 2005 |
| Yaita Plant |
January 2007 |
| Sano Plant |
April 2007 |
| Tanuma Plant |
November 2006 |
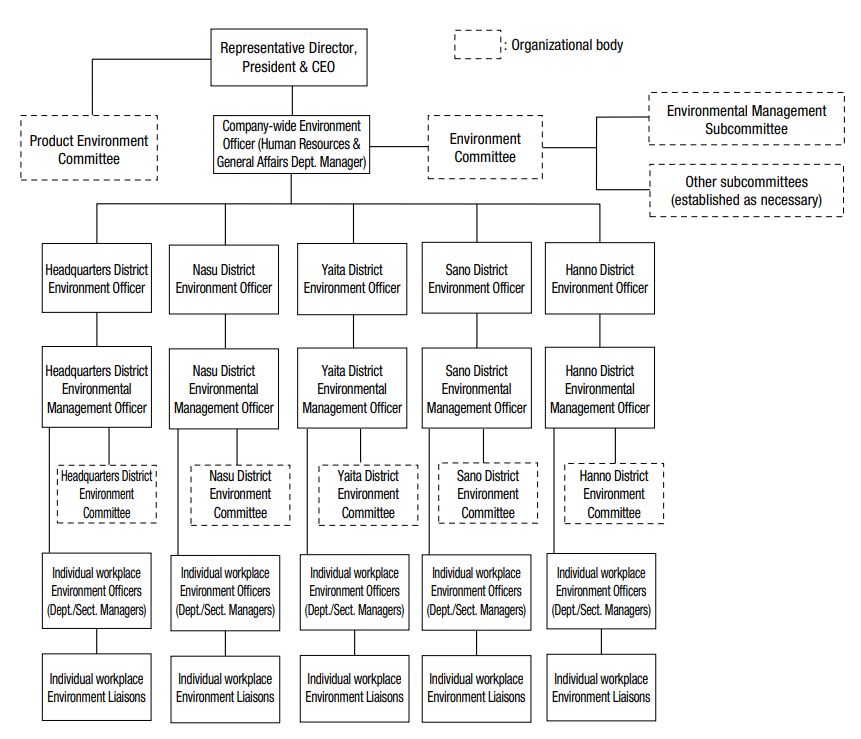
|Environmental management structure
The Environment Committee is in charge of the Group’s environmental policy, and the
Environmental Management Subcommittee has been established beneath it.
The head of the Human Resources & General Affairs Department chairs
both committees, and the managers of the Nasu, Yaita, and Sano plants serve as committee members.
|Climate Change Initiatives
The TOKYO KEIKI Group is working to reduce GHG emissions and promote resource
and energy conservation to minimize the impact of our business on climate
change. At the same time, we are taking steps to mitigate the impact of future
climate change on the Group’s businesses.
Initiatives on TCFD recommendations
We announced our endorsement of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) recommendations in August 2022. By comprehensively assessing the risks and opportunities that climate change poses to our business, we are incorporating adaptation and mitigation measures into our management strategies as we work to achieve TOKYO KEIKI Vision 2030.
If an initiative has a material impact on our business activities, we disclose it by such means as providing climate change-related financial information.
(1) Governance
To promote sustainability management, our Group
established the Sustainability Promotion Office and the
Sustainability Committee in June 2021. At the enter of
our Group, the Sustainability Promotion Office plans and
promotes measures involving sustainability management. The
Sustainability Committee is chaired by the Representative
Director, President & CEO and selects members from Internal
Directors and Executive Officers. It functions as a meeting
body that discusses and shares sustainability management-related policies and measures, and executes decisions
without delay across the Group. It also makes proposals
on key measures and issues progress reports to the
Management Conference and the Board of Directors.
The Sustainability Committee met five times in fiscal 2024 to deliberate on matters such as the progress of materiality initiatives and the formulation of the TOKYO KEIKI Group Human Rights Policy. The Human Rights Policy has been resolved by the Management Conference and the Board of Directors and was disclosed to the public in April 2025.
(2) Strategy
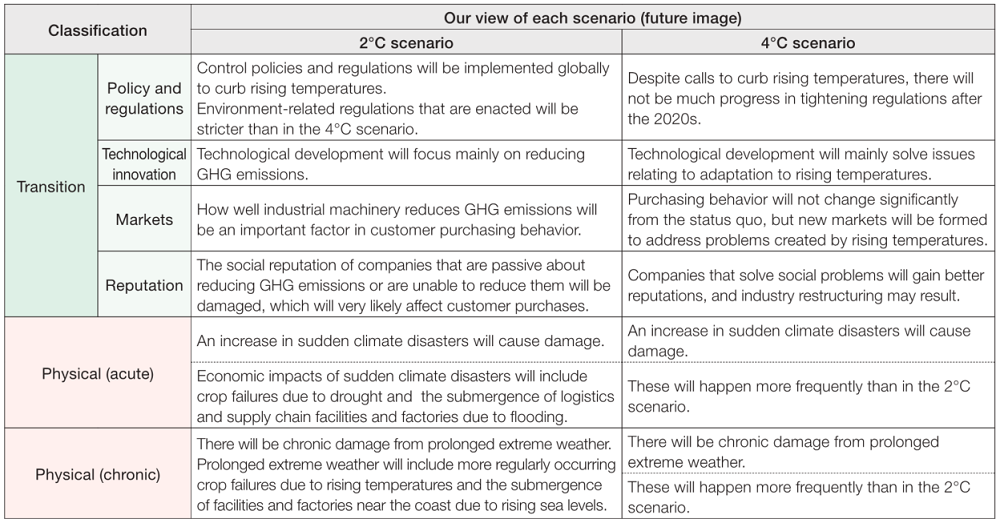
(2)-1. Scenario analysis based on TCFD recommendations
The TOKYO KEIKI Group recognizes climate change as a critical issue in the
sustainability management of the Group. For that reason, we created our own
scenarios based on the TCFD recommendations and referring to the 2°C and
4°C warming scenarios in the IPCC’s Sixth Assessment Report. Using
these scenarios, we evaluated the impact of a warmer climate in 2030, the
target year for achieving our mid- to long-term strategy. The table below
lays out our view of each scenario.
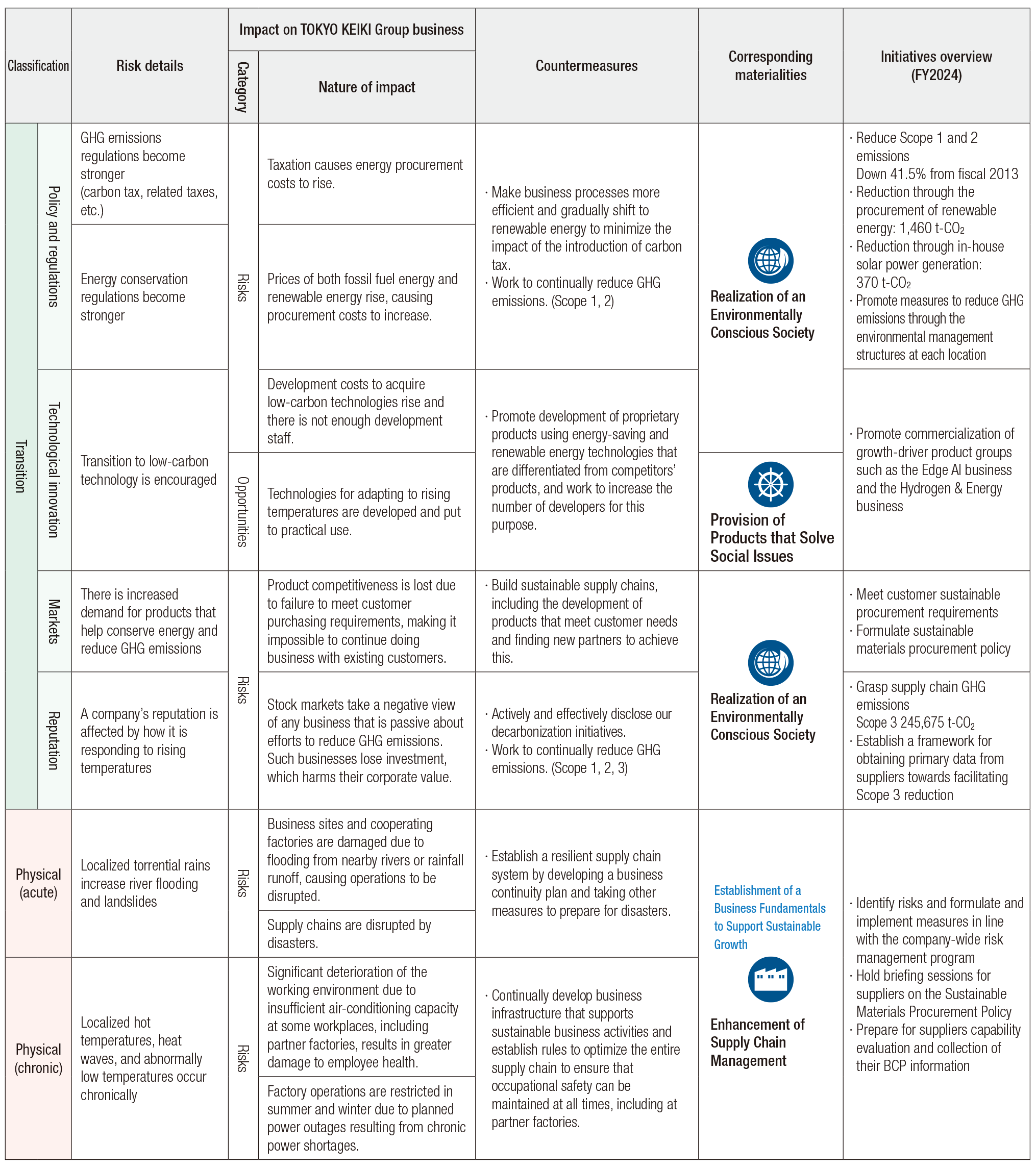
(2)-2. Assessment of risks and opportunities based on
scenario analysis and overview of initiatives
Based on the scenarios we created, we identify events
that could affect TOKYO KEIKI Group business activities
and measures to deal with them, and work on them in
materiality activities.
The table below gives an overview of initiatives in fiscal
2024. With respect to transition risks, we will continue our
initiatives to meet customer and market expectations. As
for physical risks, we are making preparations designed
to optimize the entire supply chain.
(3) Risk management
The TOKYO KEIKI Group manages risks in keeping with our risk management
system.* Following our Risk Management Rules, we classify risks as major
management risks or other risks and manage them accordingly. Risks that relate
to sustainability are written up for the Sustainability Committee’s
consideration by members of the Sustainability Promotion Office or
Sustainability Committee. The Sustainability Committee promptly discusses the
magnitude of the risks and how to deal with them. Its resolutions go to the
Management Conference and Board of Directors for deliberation and final
approval.
*See the risk management system diagram on p.88 of TOKYO KEIKI REPORT 2025.
(4) Indicators and targets
The Group set a target of reducing GHG emissions
within the Group by 37% in fiscal 2030 compared to
fiscal 2013. We are conducting activities to achieve this. In fiscal 2024, emissions totaled 7,491t-CO2, representing a 41.5% reduction compared with fiscal 2013, and remaining below the fiscal 2030 target value for the second consecutive year. Although the emission factors of electric power business operators worsened, the installation of new solar power generation facilities at the Nasu Plant and the continued procurement of electricity derived from renewable energy, etc. have contributed to an overall reduction. We will continue our efforts to achieve the targets in and after fiscal 2025 as well.
❙ Initiatives for Environmental Management
In the manufacturing industry, it is our social responsibility to try to
minimize our impact on the environment when we choose materials and use energy
to make our products. By fulfilling this responsibility while engaging in
business activities, we will contribute to the realization of a sustainable
society.
|Initiatives to reduce waste
The TOKYO KEIKI Group aims to reduce the environmental impact of various types
of waste generated when manufacturing our products. Our Group-wide efforts to
reduce such waste are based on the 3Rs concept.
Waste is disposed of appropriately in accordance with laws and government
ordinances, as well as the regulations of the municipalities where our
factories and plants are located.
We have introduced reusable containers for back-and-forth transportation with certain customers and our partner plants to eliminate the disposal of cardboard and packaging materials, etc. as waste. In addition, the use of equipment to reclaim wash oil and the evaporation and drying of wastewater from glass processing are helping to reduce the amount of wastewater and waste oil we produce.
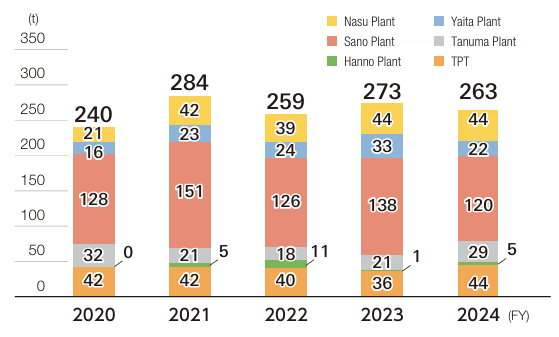
In fiscal 2024, our industrial waste output decreased by 10t year on year to 263t. We will continue to utilize environmental management to promote reduction efforts.
We are now reusing some of our used products and parts (including
electronic parts) with the approval of our customers.
We hire contractors to take our scrap metal, waste oil, and waste paper, which are valuable recyclable materials,
and accordingly thoroughly separate our waste.
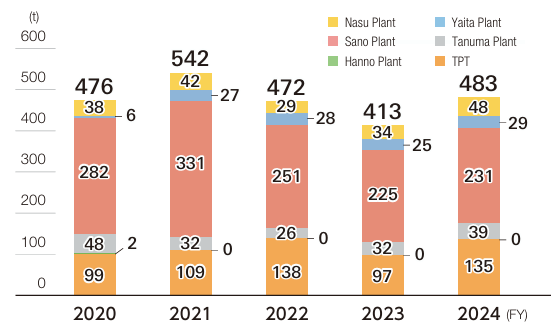
The volume of valuable recyclable materials produced in fiscal 2024 totaled 483t, with a breakdown of 406t of scrap metal, 18t of waste oil, and 59t of waste paper.
The Marine Systems Company is working in collaboration with its packaging subcontractor
TOKYO KEIKI TECHNOPORT INC. to advance initiatives aimed at reducing environmental impact. This initiative is driven by the accelerating global movement to regulate single-use plastics, especially in environmentally conscious regions such as Europe. It is also motivated by the growing trend of reusing and recycling packaging materials. In line with this global trend, we are working to establish sustainable packaging methods across our operations.
Specifically, we are replacing the plastic packaging materials for the gyrocompass, our main product, with paper-based materials. The gyrocompass is a precision instrument, so vibrations during transportation must be minimized. We are carefully selecting replacement materials while conducting thorough testing. Furthermore, we are making design changes with consideration for easy unpacking and disposal by customers.
Moving forward, we will also expand this initiative to other products, steadily implementing improvements to create a packaging system that is friendly to the environment, our customers, and our on-site staff.
|Measures for proper management of chemicals
Some chemical substances have harmful effects on the environment and human body. As such, it is companies'
social responsibility to manage them properly and to take the environment and occupational safety into account.
The Group is working to cut our emissions of chemicals by setting voluntary reduction targets.
Each of our factories is actively switching to alternative materials to hazardous chemicals.
-
Switched from dichloromethane to hydrocarbon-based.
-
Switched to alternatives free from toluene and xylene.
-
Switched to alternatives free from chlorine.
 Reduction of dichloromethane using in-house designed and manufactured cleaning unit
Reduction of dichloromethane using in-house designed and manufactured cleaning unit
|Initiatives to protect biodiversity
Another critical social responsibility for our Headquarters, plants, business
locations, and other sites as we continue our business is to reduce the impact
on the surrounding environment and work to conserve it. The Group is committed
to protecting the environment site by site in accordance with the implementation plan for its environmental management system.

 Protected forest designated by Ota Ward around the Kamata Head Office Building
Protected forest designated by Ota Ward around the Kamata Head Office Building